Cobalt
- salejandro-lopez
- 22 sept 2015
- 3 Min. de lectura

Cobalt is an essential trace element, and forms part of the active site of vitamin B12. The amount we need is very small, and the body contains only about 1 milligram. Cobalt salts can be given to certain animals in small doses to correct mineral deficiencies. In large doses cobalt is carcinogenic.
Cobalt-60 is a radioactive isotope. It is an important source of gamma-rays. It is widely used in cancer treatment, as a tracer and for radiotherapy.
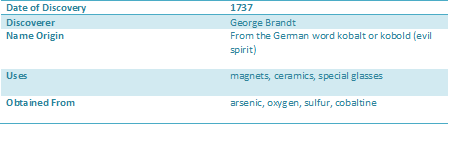
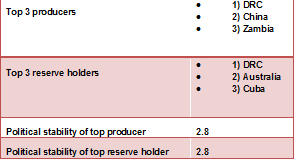
Cobalt is found in the minerals cobaltite, skutterudite and erythrite. Important ore deposits are found in DR Congo, Canada, Australia, Zambia and Brazil. Most cobalt is formed as a by-product of nickel refining.
A huge reserve of several transition metals (including cobalt) can be found in strange nodules on the floors of the deepest oceans. The nodules are manganese minerals that take millions of years to form, and together they contain many tonnes of cobalt.
Physical and chemical changes


Cobalt is a brittle, hard, silver-grey transition metal with magnetic properties similar to those of iron (it is ferromagnetic). It has a high melting point and is hard-wearing even at high temperatures. Its alloys also possess useful properties and so it finds use in high speed steels and cutting tools for instance. The physical properties of cobalt resulted in its use in a cobalt-chromium-molybdenum alloy (Vitallium, 1937) that is strong, has a good corrosion resistance and is tolerated by the body. These days cobalt alloys are used less as they are heavy.
Effects:
As cobalt is widely dispersed in the environment humans may be exposed to it by breathing air, drinking water and eating food that contains cobalt. Skin contact with soil or water that contains cobalt may also enhance exposure. Cobalt is not often freely available in the environment, but when cobalt particles are not bound to soil or sediment particles the uptake by plants and animals is higher and accumulation in plants and animals may occur. Cobalt is beneficial for humans because it is a part of vitamin B12, which is essential for human health. Cobalt is used to treat anaemia with pregnant women, because it stimulates the production of red blood cells. The total daily intake of cobalt is variable and may be as much as 1 mg, but almost all will pass through the body unadsorbed, except that in vitamine B12. However, too high concentrations of cobalt may damage human health. When we breathe in too high concentrations of cobalt through air we experience lung effects, such as asthma and pneumonia. This mainly occurs with people that work with cobalt. When plants grow on contaminated soils they will accumulate very small particles of cobalt, especially in the parts of the plant we eat, such as fruits and seeds. Soils near mining and melting facilities may contain very high amounts of cobalt, so that the uptake by humans through eating plants can cause health effects. Health effects that are a result of the uptake of high concentrations of cobalt are:

Health effects may also be caused by radiation of radioactive cobalt isotopes. This can cause sterility, hair loss, vomiting, bleeding, diarrhoea, coma and even death. This radiation is sometimes used with cancer-patients to destroy tumors. These patients also suffer from hair loss, diarrhea and vomiting.
Cobalt dust may cause an asthma-like disease with symptoms ranging from cough, shortness of breath and dyspnea to decreased pulmonary function, nodular fibrosis, permanent disability, and death. Exposure to cobalt may cause weight loss, dermatitis, and respiratory hypersensitivity. LD 50 (oral, rat)- 6171 mg/kg. (LD50 = Lethal dose 50 = Single dose of a substance that causes the death of 50% of an animal population from exposure to the substance by any route other than inhalation. LD50 is usually expressed as milligrams or grams of material per kilogram of animal weight (mg/kg or g/kg).)
Carcinogenicity- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) haslisted cobalt and cobalt compounds within group 2B (agents which are possibly carcinogenic to humans). ACGIH has placed cobalt and inorganic compounds in category A3 (Experimental animal carcinogen- the agent is carcinogenic in experimental animals at a relatively high dose, by route(s), histologic type(s), or by mechanism(s) that are not considered relevant to worker exposure.) Cobalt has been classified to be carcinogenic to experimental animals by the Federal Republic of Germany.

Isotopes

Facts:
Importance in the body:

Cobalt is used in many alloys (superalloys for parts in gas turbine aircrafr engines, corrosion resistant alloys, high-speed steels, cemented carbides), in magents and magnetic recording media, as catalysts for the petroleum and chemical industries, as drying agents for paints and inks. Cobalt blue is an important part of artists' palette and is used bu craft workers in porcelain, pottery, stained glass, tiles and enamel jewellery. The radioactive isotopes, cobalt-60, is used in medical treatment and also to irradiate food, in order to preserve the food and protect the consumer







Comentarios