Aluminium
- salejandro-lopez
- 22 sept 2015
- 3 Min. de lectura

Basic information:
Physical and Chemical properties:

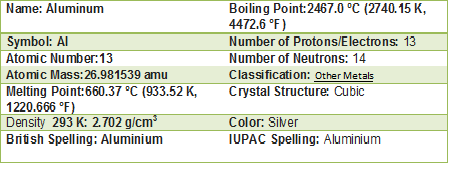
The aluminium is a metal located the block p, in the group 13 or IIIA. The chemical symbol is Al. The atomic number is 13. The atomic weight is 26.982. The key isotope is Al. It has a valance of 3.
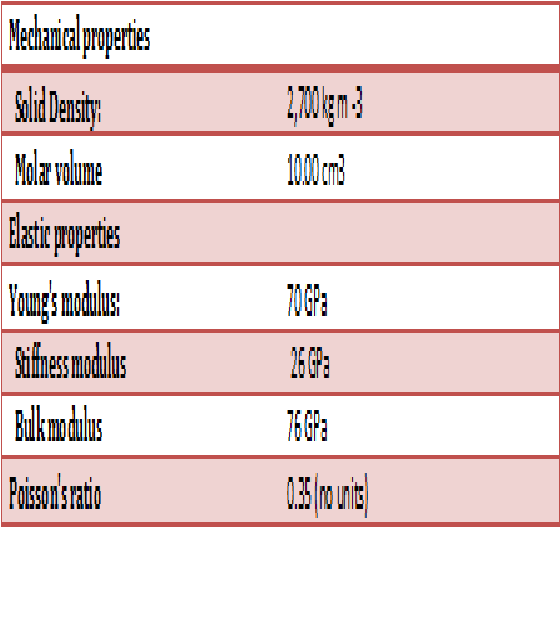
In room temperature is in solid state. The melting point is of 660.323°C (1220.581°F, 933.473 K); and the boiling point is 2519°C (4566°F, 2792 K). The density is low, it is of 2.7 . The electronegativity is 1.61. Aluminium is a silvery-white, lightweight metal. It is soft and malleable.
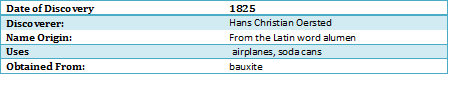
The aluminium can be found and used in cans, foils, kitchen utensils, window frames, beer kegs and airplane parts.
The aluminium is the most abundant metal in the earth (8.1%). It was discovered by the Danish Hans Oersted, in 1985.
The three higher producers are Brazil, Australia and China. An the higher reserve holders are in Guinea, Australia and Brazil.
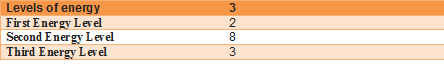
Atomic structure:
Isotopes:

Facts:
Effects:
The possibility that aluminum may have some connection with the development of Alzheimer's disease, so far discarded for lack of evidence, has become seriously raise an article published in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry. This paper summarizes the results of the autopsy of a British woman, Carole Cross, who died 58 years old and suffered a very rare form of Alzheimer's, dementia with very rapidly progressive and fatal results. Diet as the main route of exposure Many plants naturally accumulate aluminum, one of the most abundant metals on the planet The authors question that this work is not whether aluminum is a trigger for the disease, but to what extent can compare an extreme case like this, because a pollution point of high amounts, with chronic exposure to small amounts of aluminum from the diet. Are the ingested dose of aluminum concern? So far, all the evidence points to anyone. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the average adult has, through food, about five milligrams of aluminum. The food is the main route of exposure and, contrary to what one might think, the water does not bring large amounts of this metal: with concentrations of 0.1 milligrams per liter of tap water, would only 4% of the total intake aluminum. Studies in different countries have shown an average consumption of total aluminum four milligrams, where the lowest energy (for example, Japan and Australia), up to 11 milligrams, at the other end (Germany). Always below the maximum tolerable upper intake established by the Joint FAO / WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) Mixed Commission, which is seven milligrams per kilo of weight, equivalent to 60 milligrams daily for a person weighing 60 kilos. Aluminium is one of the most abundant on earth metals, so that many plants have accumulated naturally. Potatoes, spinach and tea products are high in natural aluminum. Processed foods that include aluminum additives, such as acid sodium aluminum phosphate, used in prepared foods are also an important contribution of this compound. There may be cases of increased consumption, warns WHO, usually in people taking antacids and painkillers that contain this compound, which can increase the intake of five grams of aluminum per day. Another route of exposure is through the aluminum cookware, but experts warn that aluminum is in insoluble form and the amount is so small that it would provide only impact the total consumption. Yes, as long as there is no food like tomatoes or rhubarb is cooked with acids that dissolve the surface layer of metal oxide
Importance in the body:
Aluminum is very important, since it intervenes in the enzymatic process and is related to the succinic dehydrogenase that is a transporter of oxygen necessary for the body. Also helps to intensify the reactions of cytochrome. (4) Positively intervenes in the state of ossification (bone or become acquire a consistent organic tissue) (2), of fetal tissues and acts on the cartilage of the articular surfaces and in the central nervous system, chelates with amino acids and is in transaminases. Among other benefits that we know of aluminum:
Regulates sleep It increases brain vitality aluminum deficiency causes alterations similar vitamin B, and decreases the activity of dehydrogenase Aluminum is a substance that must be present in your body because it gives you different benefits, this will have to carry out a varied diet in which no missing meats, fruits, vegetables and dairy. The values of higher aluminum plating on the body of any person have in the ovaries, testes, liver and lungs. Now, it is critical that you know through a lot of research found that people who do not have in your body sufficient amounts of aluminum can suffer different disorders as analogous alterations of vitamin B or decreased activity succinic dehydrogenase among other things. Benefits of aluminum in the body:

Relative Risk supply:








Comentarios