Amygdalin
- salejandro-lopez
- 22 sept 2015
- 1 Min. de lectura
Basic information:

This Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) information summary provides an overview of the use of laetrile as a treatment for people with cancer. The summary includes a history of laetrile research, a review of laboratory studies, the results of clinical trials, and potential side effects of using laetrile.
This summary contains the following important information:

Structure:

Formule:

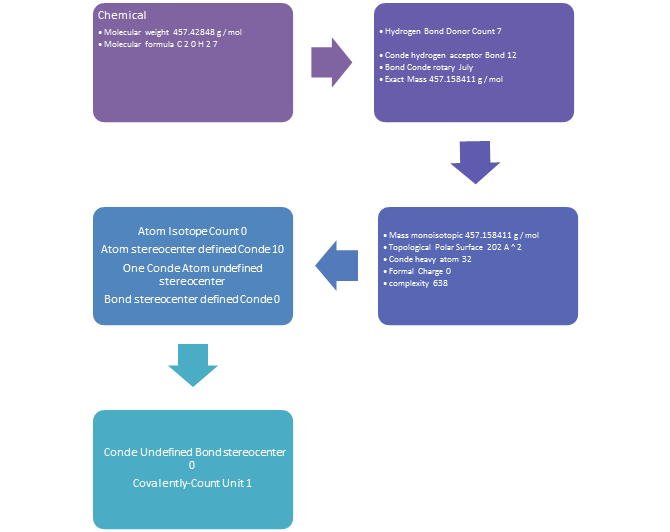
Physical and chemical propeties:

Importance in the environment:
Amygdalin is also known as laetrile, amygdalin or nitrilosida, although these compounds do not refer to a single chemical entity. The ortomedicina the called vitamin B17, but in reality it is not a vitamin. It consists of two units of glucose (sugar), a unit of benzaldehyde and one of cyanide, closely linked. To be linked within the B17 molecule, the latter two become totally inert and without effect on living tissue. Being in the presence of healthy tissue with abundant enzyme rhodanese, it neutralizes the cyanide and transforms it into products that generate beneficial nutrients to the body; in turn, oxidizes the benzaldehyde and becomes a non-toxic compound: benzoic acid. In overdose, this substance may be hazardous. It is found naturally in the seeds of apricot (apricot, apricots), apples, grapes, watermelons, and certain nuts, particularly almonds. This glycoside was initially isolated from seeds of the tree Prunus dulcis (almond). The ortomedicina initially associated with the cure for cancer, named vitamin B17, but studies have shown that lacks any effectiveness for it.
History :

Adverse effects:








Comentarios